Cause of type 1 diabetes:
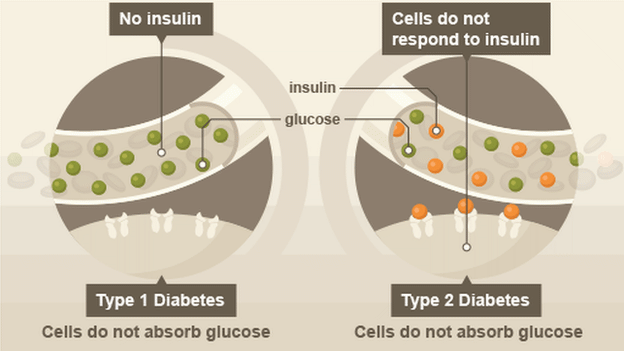
Type 1 Diabetes is due to an absence of insulin secretion by the pancreas from birth. Most of the cases of type 1 diabetes are caused by unknown triggers which results in varying amounts of destruction of beta cells in a genetically susceptible person. However, in some cases the pancreas can be damaged by auto immune diseases in which the body cells are destroyed by some cells due to unknown causes. A simple viral fever may cause the virus to attack the heart or pancreas leading onto diabetes.
Younger adults will show slower destruction of the β cells in comparison to younger children .
There are plenty of Type 1 Diabetic patients who are living well into the nineties. They all went through a tough time when diabetes management was at a very primitive stage. There were no sophisticated blood glucose monitors, no good hospitals or technology to support them, no education materials, no support groups or no insulin as well. People had to monitor the urine and be on a starvation diet to try and find a cure for this. Insulin changed the way these patients handled life. The people who have lived long to see the 2 world wars, have told they have learned this from life: “ Learn to live in spite of having Diabetes” and “take one step at a time” and “Live life to its fullest- enjoy every moment of it and thank the Almighty”.
Today there are so many advances in the field of science which brought about the discovery of insulin, the glucometer devices which could even store data of previous readings, smart phones which could guide one to monitor ones diet, remind to take medicines and even plot their progress, have alternate sources to deliver insulin, alternate devices to check sugar levels painlessly and stem cell therapy and transplantation of the pancreas.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus used to be called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. It used to be associated with children alone. There are a lot of young people and adults who are being diagnosed as having type 1 diabetes.
Clinical findings:
Those people who lose weight dramatically, do not thrive properly, get admitted for vomiting and abdominal pain are found to have diabetes mellitus type 1. It is generally seen younger the patient at time of diagnosis of diabetes, higher the chances of having type 1 diabetes. There are some people who are diagnosed with diabetes when they visit the hospital with either failing vision or kidney problems. There is a higher incidence of young adult presenting with type 2 diabetes as well.
Blood tests such as GAD 65 antibodies ( Glutamate acid decarboxylase), IAA ( Insulin auto antibodies), ICA ( Islet cell antibodies) , are some of the commonly used tests run to diagnose type 1 diabetes. However, all these may not be positive in the early stages as that depends on the damage to the islet cells of pancreas. The estimation of Insulin levels and its precursor, C peptide done in fasting and after food are also used to define type 1 diabetes.
Though many genetic markers have been identified, the widespread use of genetic screening is yet to be justified and implemented
Insulin still remains the mainstay of treatment and is usually a lifelong. There is no magic cure yet for Type 1. However, research is still on to the efficacy of a stem cell therapy. Islet cell transplantation and pancreas transplantation have also been done at selected centers round the world, but the prohibitive costs, the post transplantation medications to reduce the rejection and the uncertainty of life long cure have not led to much enthusiasm.
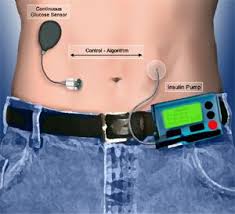
There are advances coming up in the self monitoring devices and also novel ways to administer insulin.
Young adults or children must be informed about a partial remission of the diabetes where either a low dose of insulin or no insulin may be needed in the early phase. This is called the “honeymoon” phase of diabetes when there will be some activity of the pancreas but not enough to maintain sugar levels.
Insulin :
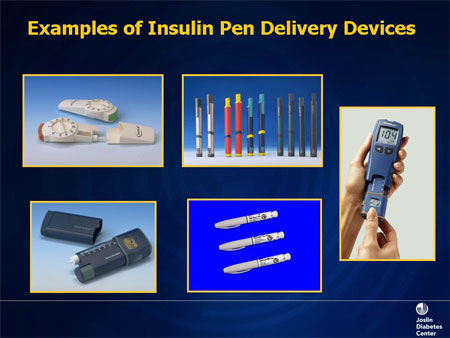
One has to take multiple injections a day to match the food intake just because the pancreas refuses to secrete insulin which keeps the sugars down. Some may need to take a combination of long acting insulin at night time and one with each main meal of the day. There different insulin preparations which have been detailed in the post titled,”insulin in diabetes”. Insulin can be given by pens which are easy to use and have small needles. Some patients may need multiple doses. Some may need insulin to be administered by a pump which delivers insulin in small doses based on food intake and physical activity.
- Insulin has to be stored in the refrigerator ( not the freezer compartment) when not in use.
- Never skip a dose of insulin as the sugars may increase and cause even an unconscious state which can kill if not treated in time.
- Likewise, if you inject too much, the sugars can drop to dangerously low levels and can make you unconscious and can kill.
- Have a sugary drink or sugar at hand always.
- When you feel sweating or shivering, it can mean the sugars are low.
- Remember to change the needles daily.
- Rotate the site of injection daily. These can be given on the thighs and abdomen. Pinch a fold of skin and inject at right angles. Do not inject if the skin is too hard on pinching or dark in color. Normally the rapid acting insulin is given on the abdomen and the long acting given on the thighs.
- When sick, it is a common mistake to either reduce the dose of insulin or omit the dose as there is reduced food intake. However when sick, the hyperglycemia demands a slightly higher dose of insulin.
- Teenage girls can have eating disorders and may omit the dose of insulin with a hope to control their weight, with grave consequences.
- As you grow up or have stress during exams, job interviews, marriage or family matters, the sugar levels can increase. As you grow up, the insulin levels will also increase.
- If having a party or attending a buffet, you are allowed to take insulin in two separate doses like 30% before the party and 70% after the party. If you take 30 units at night of rapid insulin, take 10 units before the party and 20 units after the party to cover the food intake.
- Be careful of alcohol intake and dancing after that as the sugars can drop down.
Advantages of insulin pumps over multiple daily injections :
• Ease of calculation
• Less insulin stacking
• More reliable
• Very low doses 0.01U to 0.025 can be given in those using the pump.
• Fewer skipped doses
• Less hassles with time zones
• Discreet insulin delivery
Requirements before embarking on insulin pumps:
• Should be willing to check blood glucose many times and should be able to count carbohydrates
• In toddlers, the pump can be placed between the shoulder blades or butt.
• The tip of the cannula of the infusion tubing can be blocked by the inflammatory cells causing errors in dosing.
• The settings in a young child should have high and wider range, in those with hypo unawareness, set the hypoglycemic setting higher, and those who are pregnant, set the narrower and lower range.
The accessories have to be changed once every 3 days. This is a costly matter.
Checking the blood glucose:
You need to check sugar levels quite frequently. Ideally, a pre meal and 2 hour post meal sugar check will be needed.( 7 tests a day) This will have to be done at the initial stages till you know the “signals” your body sends. Some have to check their sugars when they have had a new food or while at a party. There are machines that require a lot of blood sample for the testing and some which need very less. The finger pricks are done at the tips ( in medical terms, the pulp) of the fingers. This is a very sensitive area and the repeated pricks for the rest of your lives can affect the sensation of these wonderful parts. You will need to have a glucometer machine that will check the blood sugar and blood ketones as well. Most of the machines have data storage facilities and also some can be connected to a network and data can be transferred to a remote system such as ones parents or doctors or nurse. ( Read more of this in the post titled, Diabetes and Digital age )
Self monitoring of blood glucose can help detect low sugar or high sugar levels, help titrate the dose of insulin, can be used to assess sugar levels when sick or pregnant and also to check how the levels are after a workout.
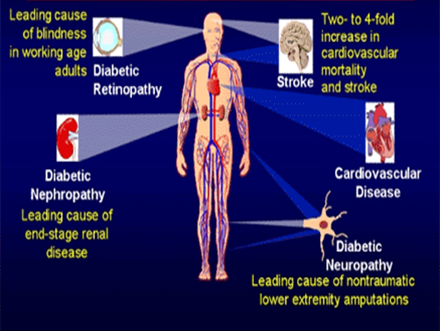
Earlier good control of sugar levels will delay the onset of the feared complications of diabetes such as the retinopathy ( eye) , neuropathy( nerves), nephropathy( kidney), heart disease.
The variability in sugar readings are more important than a stray high reading.
Good sugar control will lead an improvement of
• 76% in incidence of retinopathy
• 47-54% reduction in progression to severe eye problems
• 39% reduction in onset of microalbuminuria
• 54% reduction in onset of kidney diseases
• 60% reduction I onset of developing neuropathy
• 42-57% reduction in onset of heart related diseases.
Barriers to achieving good control:
• Fear of hypoglycemia ( low sugar)
• Complexity of day to day management
• Need for frequent self check of sugar levels
• Lack of social and family support
• Lack of specialized care access
• Increased costs
• Psychological factors- depression and anxiety
Educational programs such as DAFNE ( Dose Adjustment For Normal Eating habits) help in flexible plans for diet which help to overcome the rigid dietary control and fixed doses of insulin. There are many such good educational tools. The Conversation Maps© by Lilly is an interactive tool which helps understanding the disease well.
Periodic Check up:
The parents will accompany the child to get more understanding of the management. It is important to have the eyes checked, the feet checked and urine checked for microalbumin leak once annually after the age of 12 years. It is important to check the blood pressure and lipid profile if above 12 years of age. The 3 month average of sugar, HbA1C is to be done thrice a year. The most recent guidelines state a 3 month average sugar level of 7.5% for any age of child till the age of 18. The values were higher in the previous years.
Complications:
The complications are the same as those which a person with type 2 diabetes can have. The success of the quality of life depends on the near normal levels one can attain. It can get frustrating and depressing at times and definitely may even lead to quarrels with parents. They are concerned about the good health, though some parents may become over protective. Having high blood glucose can poison the body and slow it down! It can affect studies as well. Diabetes can affect the kidneys, eyes, heart, nerves and sensation of the limbs. Maintaining near normal sugars is the key to success to prevent these complications. Regular check up with the doctor or nurse can help lead a near normal life. If there is a problem such as difficulty in seeing while at class, please inform the teacher or parents. They may not understand the magnitude of the problem and may think it is way of escapism. Most of the schools have a medical wing having a trained nurse. A note from the health care provider can help the school authorities to take care. The child should be allowed to snack if low sugar levels are detected while in class, must have their parents notified in an emergency, but must not be restricted from regular playing and activities.
Take care of the feet- use footwear all the time even while on the beach. You may accidentally cut yourself which can take a long time to heal. Check your feet daily. Use cotton socks and use one size extra large footwear. Use a moisturizing cream on the feet taking care not to apply it between the toes. If you cannot feel either hot or cold sensations, please mention to your doctor or nurse urgently.
Take care of the eyes and tell your parents or your teacher if there is a problem. They can guide you to the doctor or nurse. Remember that eyes can get cloudy when the sugar levels increase.
Brush the teeth well and take care of them by visiting the dentist once annually.
Exercise:
 You can exercise like other people. You may tire easily. Before exercising, check your sugar levels , if high, check on blood ketone levels as well. Do not exercise if low sugar levels are seen on checking. If blood ketone levels are more than 1.5 mmol/L, give yourself 15% of the basal insulin with a pen separately. Drink a glass of non sugar drink every hour. Check again after an hour. If not feeling well, losing consciousness or dehydrated or vomiting with abdominal pain, go immediately to the hospital.
You can exercise like other people. You may tire easily. Before exercising, check your sugar levels , if high, check on blood ketone levels as well. Do not exercise if low sugar levels are seen on checking. If blood ketone levels are more than 1.5 mmol/L, give yourself 15% of the basal insulin with a pen separately. Drink a glass of non sugar drink every hour. Check again after an hour. If not feeling well, losing consciousness or dehydrated or vomiting with abdominal pain, go immediately to the hospital.
Do not exercise immediately after injecting insulin as it can get absorbed soon and cause low sugars. It depends on which part of the body you inject and which group of muscles you exercise. If you inject onto thighs and go for jogging, it will be absorbed faster. If sugars are low before the exercise, have a carb snack ( biscuits or juice) before the program. Do not give bolus injections for the snacks taken to prevent low sugars.
Warm up for 5 minutes, stretch for 5 minutes and then go into activity for about 20 minutes and allow 5 minutes for cooling down. You are to drink non sugary fluids every half an hour. You can have a carbohydrate snack- a biscuit or a fruit juice to bring up low sugars. CHOCOLATES DO NOT INCREASE THE SUGAR LEVELS INSTANTLY DUE TO ITS HIGH FAT CONTENT. Preferably do not use heavy weights while exercising as it increases the pressure in your eyes which can cause a bleed into the eyes. If you go for a sprint( high intense exercise), the sugars will increase! This is due to the increase in some hormones which increase the sugar levels.
If the doctor says you have retinopathy ( eyes are affected by Diabetes), avoid lifting heavy weights and strenuous workouts.
Read more in the blog: Exercise and Diabetes
This is a medical emergency. If the blood sugars are high and if there are ketones in the blood the following can be done before going to the hospital.
Blood glucose Blood ketones Insulin dosage
>200mg% <0.6 mmol/L One unit Rapid insulin for each 50mg%above 100 Mg%
>200 mg% 0.6-1.5 mmol/L 10% of TDD of rapid insulin
>200mg% >1.5 mmol/L 20% of TDD as rapid insulin
TDD means total daily dose. To convert sugar in mg% to mmol/L divide by 18
If the blood sugar is 345 mg%, the extra insulin has to be calculated as follows:
345- 100 = 245 mg%
Give one unit for each 50mg% above 100mg%
This means you have to give 5 units of rapid acting insulin ( 245/ 50)
Check sugar and blood ketones every hour till normal. You can use the Freestyle Optium Xceed meter for this. You can place blood as for checking the sugar on the strips for ketones and sugar.
For example, if the blood glucose is 22 mmol/L, the excess is 16.5 mmol( 22-5.5) You have to give one unit rapid for each 2.7 mmol excess. This means, 16.5 / 2.7 which is equal to 6 units.
Blood sugar In mmol/L Excess sugar above 5.5 mmol/ 2.7 Extra Rapid Insulin to be given
15 9.5/2.7 3.5 units (3 u)
16 10.5/2.7 3.8 units ( 3 u)
17 11.5/2.7 4.25 ( 4 u)
18 12.5/2.7 4.6 ( 4 u)
19 13.5/2.7 5 ( 5 u)
20 14.5/2.7 5.3 ( 5 u)
21 15.5/2.7 5.7 ( 5 u)
25 19.5/ 2.7 7. 2 ( 7 u)
Remember that the first 5.5 mmol of sugar is not counted for correction. The value above that is used for calculation. So please do not give a rough 10 units for any emergency at home. The aim is to correct the excess sugar. Do not feed the child after this dose of insulin. At this dose of insulin, the child will not go into low sugar. Make the child drink water hourly. Check the sugar every 15 minutes. If vomiting or abdominal pain or losing consciousness, get the child to hospital immediately.
The TDD means the total daily dose of rapid taken in a day. If it is 6+12+8, the total is 26 units. 10% of this is 2.6 units
20% of the total daily dose is 6+12+8= 26 and 20% of this is 5.2 units.
This needs some quick calculation. The best will be to give something like 4 units insulin, then calculate the exact amount.
If hypoglycemia ( when sugar levels fall down) develops, drink orange juice or take sugar or dates. In somecountries glucose tablets are available. Wait for half an hour. Recheck and if needed take more orange juice. You can have a handful of raisins( dry grapes) also if needed.
Glucagon kits will be available in the pharmacy. This is used for treatment of low sugar levels before reaching the hospital.
If less than 8 years of age or weighing less than 25 kg give 500 mcg of glucagon Intramuscularly. If weighing more than 25 kg or more than 8 years of age, give 1 mg of glucagon intra muscularly. Check sugar levels again in 10 minutes. Take to the hospital if not better.
Adventure sports
- Having type 1 diabetes does not prevent you from enjoying life to the fullest.
- Never go for adventure sports alone.
- If going for high altitude trekking, remember high altitude trips mimic mountain sickness ( headache, intestinal discomfort and fatigue)
- Increased blood sugar and insulin resistance can occur at high altitudes. Sugar levels can fall with the increased activity.
- Glucometers may not be accurate at cold temperature; the insulin may freeze as well.
Deep sea diving:
In those who dive deep, no unconsciousness has been reported. However, it is better to check the sugar levels an hour, half an hour and just before diving.
The transition from a child to an adult

• Kids just want to be kids. Child is a child first. Diabetes comes second.
• They strive for a little more independence each year. They do not want to stand out from the crowd. How the child accepts diabetes will depend on how, you as a parent, look at it. If you feel diabetes is a tragedy, the child will feel that way as well. However if you look at it as a fact of life that requires attention and discipline, the child will be prepared for a healthier future.
• Checking sugar frequently is painful but the child will gradually understand the importance.
• Remind them to be snacking in between playing hours.
• Remind independence comes with responsibility as they grow from a child to a teen.
• If your child reports a high blood sugar, do not scold them. They may be trying their best. Shower them with praise when they do well. Remember that nobody is perfect.
• Ups and downs of sugar levels are part of growing up and changes in body hormones as they grow into their teens.
• It is worthwhile checking how each food affects the sugar before and after eating and before and after exercise.