Diabetes is becoming a household name it is as common as having a mobile phone. What was previously referred to as a disease affecting the rich and affluent is now across all social strata, irrespective of financial status, race, culture, geographical location, gender or age ! This may be the curse of the modern day living with abundant stress, automated chores, sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits caused by the food revolution.
To help fight diabetes is an uphill battle- many succeed fully , some partly and some not at all. This may be again due to multiple factors such as lack of access to healthcare, non affordability, denial of having diabetes, lack of proper awareness, lack of education and long imprinted myths and stigma associated with diabetes.
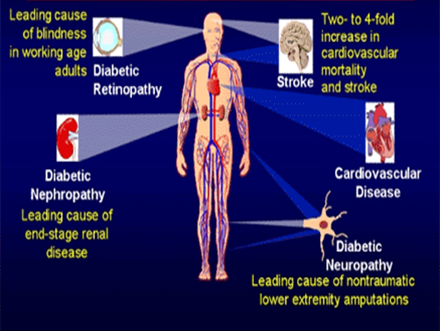
The complications of diabetes are broadly classified into 2 based on the caliber of blood vessels affected- microvascular , when small caliber vessels are involved and macrovascular when bigger caliber vessels are involved.
Diabetes is the leading cause of preventable blindness the world over. It is not that people are unaware of this; it is just that many prefer to meet the doctor only when symptomatic. The unfortunate thing about eye disease in those with diabetes is that it is asymptomatic for most of the initial phase of diabetes and by the time it becomes symptomatic more than three fourths of the eye may have been affected causing inconsistent response to treatment modalities. Most of the time, a casual check is what may help in initial diagnosis of diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels. Frequent changing of the reading glass is not a solution if having diabetes- it is wiser to consult an eye doctor and have the eyes checked to ascertain the cause.
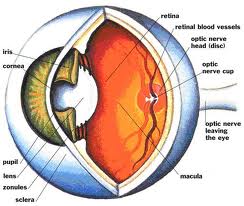
Basic anatomy: The eyelids protect the eyes from injury and also to protect from dry eyes. Eyes are also an object of beauty( the eyelashes, in particular) and women pay particular attention to eyes especially if in the media world. The white portion one sees is the sclera. At the center of the eye is a colored Iris, the center of which is the pupil through which the light enters the eyes. The pupils can dilate and contract also depending upon the light ( akin to the shutter aperture of a camera). The light after entering the pupils, then reaches the back of the eyes on a part called retina from where the signals are sent to the brain for interpretation. The eyes are kept moist by the tears secreted from time to time. The eyes become dry due to the excessive screen time, use of air conditioners, unprotected eyes during harsh sunshine, improper use of contact lenses and when working in very windy conditions.
Glaucoma is a condition where the pressure inside the eyes is high, cataract is when the lenses become opaque and hard and retinopathy is when the retina is affected by diabetes or high blood pressure.
Certain red flags
• Blurry vision- may be due to dry eyes or uncontrolled diabetes- when the sugar levels increase the fluid which houses the lens, becomes opaque which causes the eyes to lose focus. This will reverse with correction of diabetes.
• Seeing double
• Injury to eyes
• Red eyes
• Floaters
• Trouble reading
An eye check up is advisable every year (or earlier, if advised by the eye Dr) for all patients with diabetes- whether type 1 or 2. All pregnant women with diabetes must also have an eye check up done. Those with uncontrolled blood pressure or high cholesterol levels also need to have the eyes checked out.
The eye check up will involve a waiting period and one must come with someone to help driving back as the eyes will be blurry for varying periods of time such as an hour to 4 hours. There is no need to be fasting for the eyes testing. Please bring along any reading glass and the prescription and contact lenses when coming for the tests. Resting with eyes closed after the test will help prevent glare and associated headache when going out of the hospital or clinic.
The doctor or optometrist will do a reading test initially followed by instillation of drops which will help dilate the pupils so the eye Doctor can look inside the pupils to see the inside of the eye. For some, the eyes will dilate slowly and so may need more frequent instillation. One may get claustrophobic as one will have to keep the eyes closed. The eyes will be checked by ophthalmoscopy using a hand held devise with a light which will help look inside the eyes or a color fundus photography is done in centers where available and a visual field testing is done to assess the field. The pressure of the eyes will be checked by either a computer assisted devise or use of a contact appliance on the eyes. Some may need a scan of the eyes called OCT which will help show the thickness of the eye layers inside, some may need a flourscein angiogram. The Digital imaging has opened up new avenues in the early diagnosis as well as help in monitoring the progress of the condition as well. All the tests are painless, but can be very unpleasant for the patient as eyes will be blurry. A child will have a tougher time ( the doctor too !)
The duration of diabetes, the degree of high sugar levels, the presence of uncontrolled blood pressure or cholesterol levels all affect the health of the eyes. Achieving good control with compliance to medicines, adherence to lifestyle( diet, exercise, cessation of smoking and alcohol) can help delay the onset or even slow the progression of the damage.
The small vessels inside the eyes get damaged leading to small leaks, small aneurysms( out pouching of the weak vessel wall) and cut off of focal blood supply to certain areas( ischemia). If unchecked, this can progress to cutting off of blood supply to larger areas, further leaking from the vessels causing larger hemorrhage. This stage is called non proliferative stage. The eyes are asymptomatic during this stage.
• As the disease progresses, new fragile vessels are develop. These vessels can either bleed or shrink and harden. When the vessels bleed, they cause floaters where patients see blackish spots in the field of vision This stage is called proliferative (meaning multiplication- the new vessels being formed). This is symptomatic.
• .When the vessels harden it may cause separation of the retina in part or in full (retinal detachment)
• As diabetes advances even further, fluid may start forming inside layers of retina called macular edema.
There are different modalities of treatment which will be decided upon by the treating doctor. It may involve just frequent check up (if very minor changes in a well controlled person) or involve laser treatment or injections which are sometimes costly and may need multiple sittings as well.
The major challenges facing the eye care team these days is the tremendous increase in prevalence of diabetes, the increased cases of diabetes among the young population and carelessness of the patients by neglecting symptoms or red flag signs.
The aim of treatment will be in preventing the progression to proliferative disease, prevent or delay the onset of complications which may in turn, lead to vision loss.
The next modality of treatment will be aimed at preventing or eleminating fluid in the macula. A class of medicines called Anti VEGF ( Ranibizumab or biosimilars, Aflibercept or Bolucizumab) are used when necessary. Steroids may sometimes have to be administered.
Research is going on studying the benefits of using VEGF Gene therapy, monoclonal Antibodies, Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor, Integrin inhibitors, Plasma Kalikrein inhibitors, senolytic inhibitors and REdox signalling and repair agents.